Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Business Intelligence (BI)
Business Intelligence (BI) refers to technologies, tools, and practices that allow organizations to gather, analyze, and utilize data effectively. Through data analytics, BI offers insights that help companies make more informed decisions, manage risks, and adapt to changing market conditions.
Importance of Decision-Making in Business
In a business environment, decisions range from long-term strategic choices to quick daily operations. The quality of these decisions can significantly impact the success and growth of the organization. This is where BI becomes invaluable by providing accurate, timely information to aid in decision-making.
Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!


Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!
How Business Intelligence Supports Decision-Making
BI systems are equipped with capabilities to analyze large datasets and identify patterns, trends, and outliers. This analysis provides leaders with a comprehensive understanding of current and potential future scenarios, enabling them to make more accurate and reliable decisions.
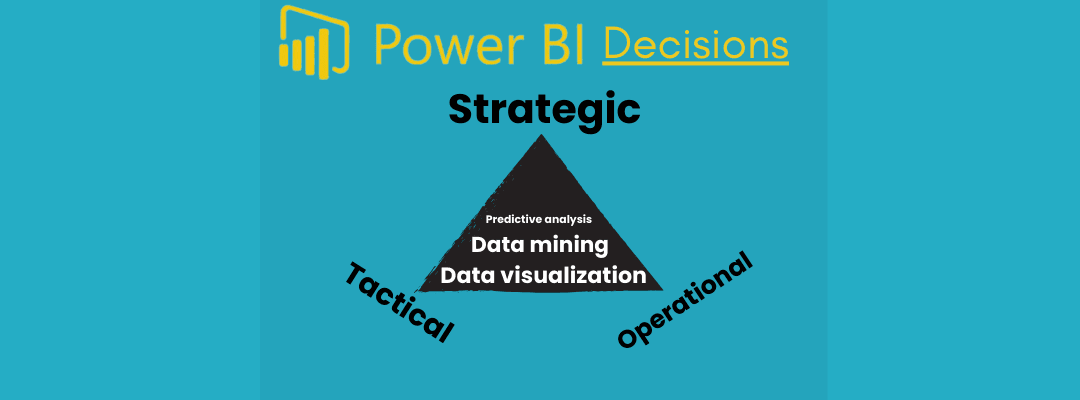
Types of Decisions Supported by BI
Business Intelligence supports three primary types of decision-making:
4.1 Strategic Decisions
These are high-level decisions that define the overall direction and goals of an organization, such as entering a new market or launching a new product.
4.2 Tactical Decisions
These decisions focus on the intermediate term and are concerned with implementing strategies, such as optimizing marketing campaigns or adjusting pricing strategies.
4.3 Operational Decisions
Operational decisions deal with the day-to-day functioning of the organization, like managing inventory levels or scheduling employees.
Strategic Decision-Making and BI
5.1 Defining Strategic Decisions
Strategic decisions shape the future path of the company and often involve long-term commitments. These decisions are critical as they affect the entire organization and set the foundation for future growth.
5.2 How BI Assists in Strategic Decisions
BI helps leaders analyze historical trends and forecast future outcomes. This enables leaders to make proactive strategic decisions by evaluating risks and opportunities effectively.
Examples of BI in Strategic Decision-Making
For instance, BI might help a retail company analyze consumer purchasing trends over the past decade to predict future demands. This analysis assists in making strategic decisions like expanding product lines or entering new markets.
Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!


Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!
Tactical Decision-Making and BI
7.1 Defining Tactical Decisions
Tactical decisions bridge the gap between strategic objectives and day-to-day operations. They are focused on achieving short- to medium-term goals.
7.2 Role of BI in Tactical Decisions
With BI, organizations can optimize their resources and make tactical adjustments in areas like pricing, promotions, and production processes, thus improving efficiency and profitability.
Examples of BI in Tactical Decision-Making
A company can use BI tools to evaluate the effectiveness of various marketing campaigns by examining real-time data. This allows for adjustments to improve campaign performance and better target customer segments.
Operational Decision-Making and BI
9.1 Defining Operational Decisions
Operational decisions deal with routine activities essential for daily business operations. These decisions focus on efficiency and maintaining smooth workflows.
9.2 How BI Enhances Operational Decisions
BI can streamline these day-to-day activities by providing data that helps teams make quick and accurate decisions regarding logistics, customer service, and inventory management.
Examples of BI in Operational Decision-Making
For example, an e-commerce company might use BI to track stock levels and automatically order more inventory when supplies are low, ensuring that products are always available to customers.
Benefits of Using BI for Decision-Making
- Data Accuracy: BI ensures that decisions are based on accurate data, reducing the risk of errors.
- Improved Efficiency: BI systems automate data gathering and processing, saving time and resources.
- Better Forecasting: By analyzing past data, BI provides valuable insights that improve future planning and forecasting.
Challenges and Considerations in BI-Driven Decision-Making
Despite its benefits, implementing BI comes with challenges, such as data quality issues, integration complexities, and ensuring data security. Businesses must have a solid data governance strategy to maximize the potential of BI tools.
Real-World Applications of BI in Different Industries
- Healthcare: BI supports clinical decision-making, optimizing patient care.
- Retail: BI aids in managing inventory and analyzing customer behavior.
- Finance: BI tools help in risk assessment and fraud detection.
Future of BI in Decision-Making
As AI and machine learning continue to evolve, BI systems will become even more advanced, allowing businesses to make decisions faster and with greater accuracy. Future BI trends may include predictive analytics and real-time decision support systems.
Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!


Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!
FAQs
1. What is Business Intelligence (BI)?
Business Intelligence is a set of tools and techniques that analyze data to help businesses make informed decisions.
2. How does BI support strategic decisions?
BI assists in strategic decision-making by providing insights into historical trends and forecasting future scenarios.
3. Can BI help with day-to-day decisions?
Yes, BI supports operational decisions, helping businesses manage tasks like inventory, scheduling, and logistics.
4. What industries benefit the most from BI?
Industries like healthcare, finance, and retail benefit greatly from BI, as it helps optimize operations, improve customer service, and manage risks.
5. What challenges are associated with BI?
Challenges include data quality issues, integration complexities, and ensuring data security.