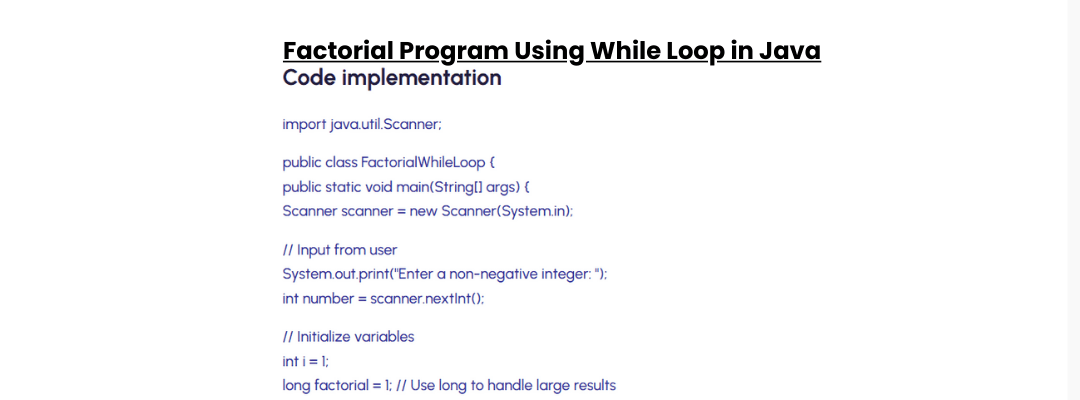
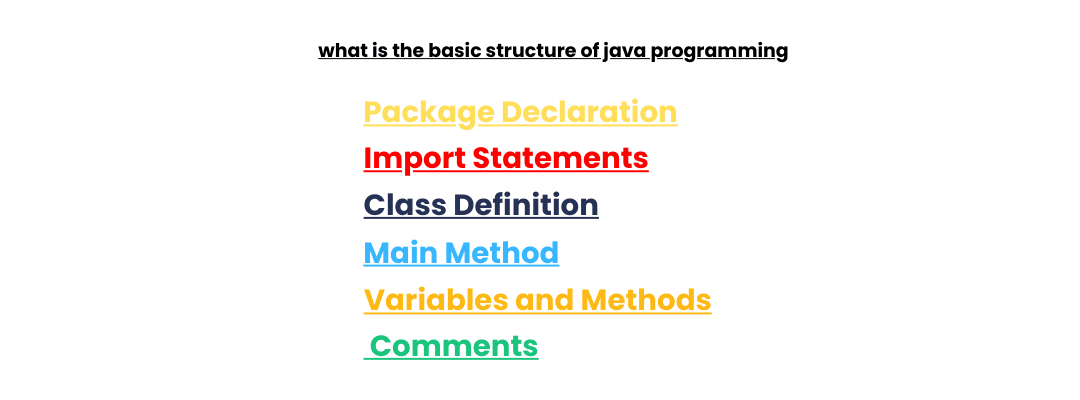
What Are Three Examples of Deadlocks?
Deadlock in DBMS is a concept every database administrator and developer needs to understand thoroughly. Imagine you’re stuck in a gridlock on a busy road where no car can move forward or backward—deadlocks in a database are no different. In this article, we’ll explore the three most common examples of deadlocks, their causes, and how to prevent them.
Understanding Deadlock in DBMS
What is a Deadlock?
A deadlock occurs when processes block each other by holding onto resources the other processes need. Think of it like two people trying to pass through a narrow hallway simultaneously—they’re both stuck until one steps aside. In DBMS, this can cripple your database operations, leading to frustration and delays.
Key Terms Related to Deadlocks
- Resource Locking: The process of securing a resource for exclusive use.
- Mutual Exclusion: Ensuring only one process uses a resource at any given time.
Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!

Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!
Example 1: Circular Wait
What Causes Circular Wait?
Circular wait occurs when processes form a cycle where each one is waiting for a resource held by the next in the circle. It’s like playing musical chairs, but no one moves.
Real-Life Example in Databases
Imagine Transaction A holds Resource 1 and needs Resource 2, while Transaction B holds Resource 2 and needs Resource 1. This circular dependency causes both transactions to halt indefinitely.
Example 2: Hold and Wait
How Hold and Wait Leads to Deadlock
Hold and wait happens when a process is holding one resource and waiting to acquire additional ones. This leaves the resources in limbo, blocking other processes.
Illustration in DBMS
Consider a scenario where a transaction locks a table for writing but also needs access to another table locked by a different transaction. Neither can proceed, resulting in a deadlock.
Example 3: No Preemption
What is No Preemption in Deadlocks?
No preemption means a resource cannot be forcibly taken from a process—it must be voluntarily released. This can lead to a standstill when processes refuse to let go.
Practical DBMS Scenario
For instance, if a process locks a critical row and doesn’t release it due to an error, other dependent processes will remain stuck.
How to Detect and Resolve Deadlocks
Deadlock Detection Techniques
- Wait-for Graph: A visual representation of resource allocation.
- Deadlock Detection Algorithms: Algorithms used to identify cycles indicating deadlocks
Methods to Resolve Deadlocks
- Transaction Rollback: Reverting one or more processes to free up resources.
- Resource Reallocation: Adjusting the allocation to break the cycle.
Preventing Deadlocks in DBMS
Deadlock Prevention Techniques
- Avoid circular waits by enforcing resource acquisition in a specific order.
- Limit the number of resources a process can hold.
Best Practices for Database Management
- Regularly monitor your database.
- Use timeout settings to automatically resolve potential deadlocks.
Common Tools to Handle Deadlocks
Built-in DBMS Features
- MySQL’s InnoDB automatically detects and resolves deadlocks.
- SQL Server’s Deadlock Graph offers visual insights.
Third-Party Tools
- Tools like SolarWinds Database Performance Analyzer can identify and prevent deadlocks efficiently.
Conclusion
Deadlocks in DBMS can be challenging but are manageable with the right strategies. Understanding examples like circular wait, hold and wait, and no preemption can help you identify and resolve them proactively. Always keep your database processes streamlined to avoid unnecessary conflicts.
FAQs
What is a deadlock in DBMS in simple terms?
A deadlock occurs when two or more processes block each other by holding onto resources the other processes need. Think of it as a standstill in traffic.
How does circular wait lead to a deadlock?
Circular wait creates a loop where each process is waiting for a resource held by the next, resulting in a stalemate.
Can deadlocks occur in distributed databases?
Yes, deadlocks can occur in distributed databases due to resource contention across nodes.
What tools can help detect deadlocks?
Tools like SQL Server Deadlock Graph and SolarWinds DPA are great for detection.
How can I prevent deadlocks as a beginner in DBMS?
Start by implementing resource acquisition order and using timeout settings to avoid conflicts.
Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!