Factorials are a fundamental concept in mathematics, often used in programming. Whether you’re a beginner or prepping for an interview, mastering a factorial program in Java can give you a competitive edge.
Table of Contents
ToggleLets Discuss Factorial of a Number in Java
What is a Factorial?
A factorial is the product of all positive integers up to a given number. For example, the factorial of 5 (denoted as 5!) is calculated as:
5! = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120.
Why Learn Factorial in Java?
Understanding how to implement the factorial of a number in Java builds a strong foundation in recursion, iteration, and logical thinking—essential skills for any Java developer.
Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!

Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!
Understanding the Factorial Concept
Formula for Calculating Factorials
The formula for calculating factorials is straightforward:
n! = n × (n – 1) × (n – 2) × … × 1
For example:
- 3! = 3 × 2 × 1 = 6
- 4! = 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 24
Real-Life Applications of Factorials
Factorials are used in:
- Permutations and combinations
- Probability calculations
- Algorithm design and analysis
How to Write a Factorial Program in Java
Let’s dive into creating a factorial program in Java, step by step.
Step-by-Step Approach
- Understand the logic for factorial calculation.
- Choose between iteration and recursion.
- Implement error handling for edge cases like 0! and negative numbers.
Importance in Interview Preparation
Interviewers often ask candidates to implement a factorial using recursion in Java or optimize it. This question tests your understanding of recursion, edge cases, and efficiency.
Types of Factorial Programs in Java
Iterative Approach
In this approach, a loop is used to calculate the factorial.
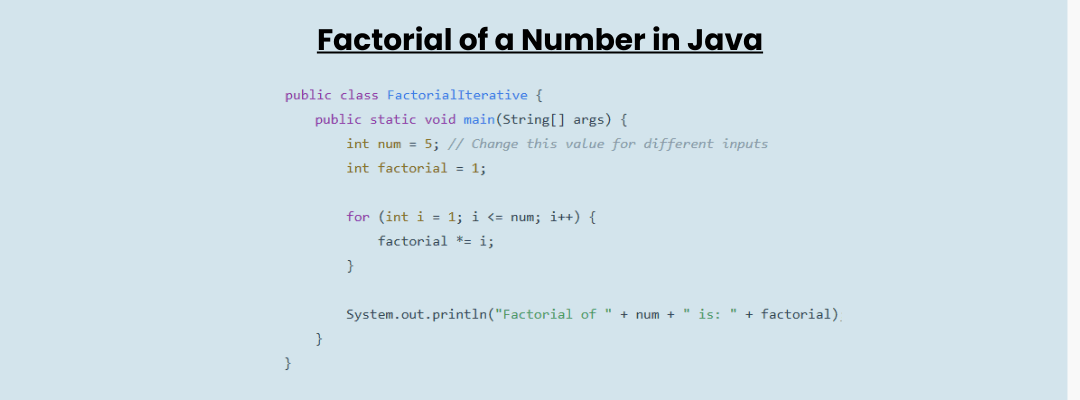
Sample Code for Iterative Factorial Program
public class FactorialIterative {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 5; // Change this value for different inputs
int factorial = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
factorial *= i;
}
System.out.println(“Factorial of ” + num + ” is: ” + factorial);
}
}
Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!


Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!
Recursive Approach
In this method, a function calls itself to calculate the factorial.
Sample Code for Factorial Using Recursion in Java
public class FactorialRecursive {
public static int factorial(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 1; // Base case
}
return n * factorial(n – 1); // Recursive call
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 5; // Change this value for different inputs
System.out.println(“Factorial of ” + num + ” is: ” + factorial(num));
}
}
Exploring Factorial Using Recursion in Java
Advantages of Recursion
- Simplifies the code
- Demonstrates the divide-and-conquer technique
Common Errors and How to Avoid Them
- Forgetting the base case leads to infinite recursion.
- Incorrect handling of edge cases like negative numbers.
Factorial Program in Java – A Deep Dive
Handling Edge Cases
- 0! = 1: This is a special case.
- Negative numbers: Factorial is undefined for negative numbers.
Optimizing the Code for Performance
- Use memoization to avoid redundant calculations.
- Prefer iterative methods for large inputs to save stack memory.
Advanced Concepts with Factorial in Java
Large Factorials and BigInteger
For very large inputs, use Java’s BigInteger class:
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class FactorialBigInteger {
public static BigInteger factorial(int n) {
BigInteger result = BigInteger.ONE;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
result = result.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(i));
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 50; // Example for large factorials
System.out.println(“Factorial of ” + num + ” is: ” + factorial(num));
}
}
Factorial in Java with Memoization
Memoization stores previously calculated factorials, reducing redundant computations
FAQs
1. How do you calculate the factorial of a number in Java?
You can calculate it using either iteration or recursion.
2. What is the difference between recursion and iteration for factorial programs?
Recursion is elegant but consumes more memory. Iteration is more efficient for large inputs.
3. Why is recursion preferred in certain cases for factorial in Java?
It simplifies the logic and is easier to implement for small inputs.
4. How do I prepare for factorial-related questions in an interview?
Practice both approaches, understand edge cases, and focus on optimization.
5. Can factorial in Java handle very large numbers?
Yes, by using Java’s BigInteger class.
Unlock Your Business Intelligence Potential with Power BI!